

9022070303
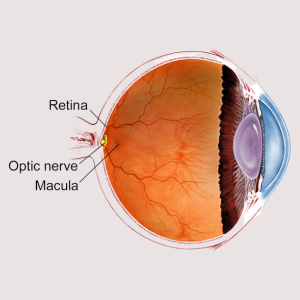
Retina
The retina is a vital part of the eye, serving as the innermost nerve layer that lines the back of the eye. Think of it as the camera film, responsible for processing the images projected onto it before transmitting them to the brain via the optic nerve. At Akshay Eye Clinic, we understand the significance of the retina and offer specialised care for various retinal conditions.
What is a retina specialist?
A retina specialist is a medical doctor who has undergone additional fellowship training in diseases and surgery of the vitreous and retina, building upon their expertise as ophthalmologists. The retina is a delicate and sensitive part of the eye, requiring specialised attention when facing any potential dangers. Damage to the retina can lead to vision loss or even blindness. Our highly skilled retina specialist, Dr. Nitin Shitut, possesses extensive experience in managing a wide range of vitreoretinal disorders.
What are the common problems associated with the retina?
1. Retinal Detachment, 2. Macular Degeneration, 3. Diabetic Eye Disease, 4. Flashes & Floaters, 5. Macular Edema, 6. Retinitis Pigmentosa
Retinal Detachment: A serious condition that can result in blindness if not treated promptly. The vitreous gel in the eye contracts as part of the normal ageing process and may pull on the retina, leading to retinal tears and detachment.
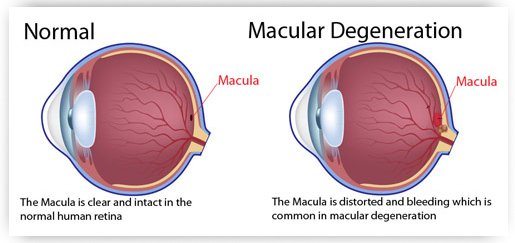
Macular Degeneration: The leading cause of severe and permanent vision loss in individuals over 60 years old. Age-related macular degeneration (AMD) occurs when the central portion of the retina, known as the macula, deteriorates over time.
Diabetic Eye Disease: People with diabetes are at risk of developing diabetic eye disease, which affects the blood vessels in the retina. This condition can lead to vision impairment or even blindness if left untreated.
Flashes and Floaters: These are visual disturbances that may indicate underlying retinal issues. Flashes appear as brief bursts of light, while floaters are small specks or cobweb-like shapes that drift across your field of vision.
Macular Edema: Swelling or fluid accumulation in the macula, leading to blurry or distorted central vision. Macular edema can occur due to various retinal conditions, including diabetic eye disease or retinal vein occlusion.
Retinitis Pigmentosa: A group of inherited disorders that cause the progressive degeneration of the retina. This condition often leads to tunnel vision or complete vision loss.
What do I do if I have been told I have issues with the retina?
If you have been informed about retina problems, macular degeneration, macular edema, diabetic eye disease, or retinal detachment, it is crucial to seek immediate consultation with a retina specialist. Retinal detachment, in particular, is a severe condition that almost always causes blindness if not treated early. As the vitreous gel in the eye changes with age, it may create tears in the retina, leading to detachment and vision loss.
Age-Related Macular Degeneration?
Understanding Age-Related Macular degeneration (AMD) is a progressive eye disease that primarily affects older individuals. It occurs when the macula, the central part of the retina responsible for clear vision, deteriorates. Although it usually does not cause complete blindness, severe vision problems can arise.
Wet vs. Dry Macular Degeneration
There are two main types of age-related macular degeneration:
Dry form
The most common type, characterised by the presence of yellow deposits called drusen in the macula. Gradual vision loss occurs as drusen grows larger and more numerous, leading to thinning and death of the light-sensitive cells in the macula. Blind spots in the center of the vision may develop, eventually resulting in central vision loss.
Wet form
Less common but more rapid in progression, wet AMD involves the growth of unstable blood vessels beneath the macula. These vessels leak blood and fluid, causing distorted vision and the appearance of wavy lines. Blind spots and central vision loss can also occur as a result. Only about 10% of individuals with macular degeneration have the wet form.
Symptoms of Macular Degeneration
In the early stages, macular degeneration may not exhibit noticeable signs. It often goes undiagnosed until it worsens or affects both eyes. Symptoms of macular degeneration may include:
• Blurry or less clear vision, making it challenging to read fine print or drive.
• Dark, blurry areas in the center of your vision.
• Rarely, changes in colour perception.
Causes
The causes of dry macular degeneration are not fully understood, but research suggests a combination of genetic factors and environmental influences such as smoking, obesity, and diet. The condition typically develops as the eye ages, affecting the macula and causing thinning and loss of vision cells.
Risk factors
Factors that may increase your risk of macular degeneration include:
• Age: This disease is most common in people over 60.
• Family history and genetics: This disease has a hereditary component. Researchers have identified several genes linked to the condition.
• Race: Macular degeneration is more common in white people.
• Smoking: Smoking cigarettes or being regularly exposed to tobacco smoke
greatly increases your risk of macular degeneration.
• Obesity: Research indicates that being obese may increase your chance that early or intermediate macular degeneration will progress to the more severe form of the disease.
• Cardiovascular disease: If you have heart or blood vessel disease, you may be at higher risk of macular degeneration.
Treatment
Currently, there is no cure for dry macular degeneration. However, certain steps can help slow down the progression of vision loss. These include:
• Avoiding smoking and exposure to tobacco smoke.
• Maintaining a healthy diet.
• Managing other medical conditions.
• Maintaining a healthy weight and engaging in regular exercise.
• Regular eye exams to monitor the condition.
Laser photocoagulation is a laser surgery technique used to treat late-stage macular degeneration. It helps prevent vision loss by sealing leaky blood vessels.
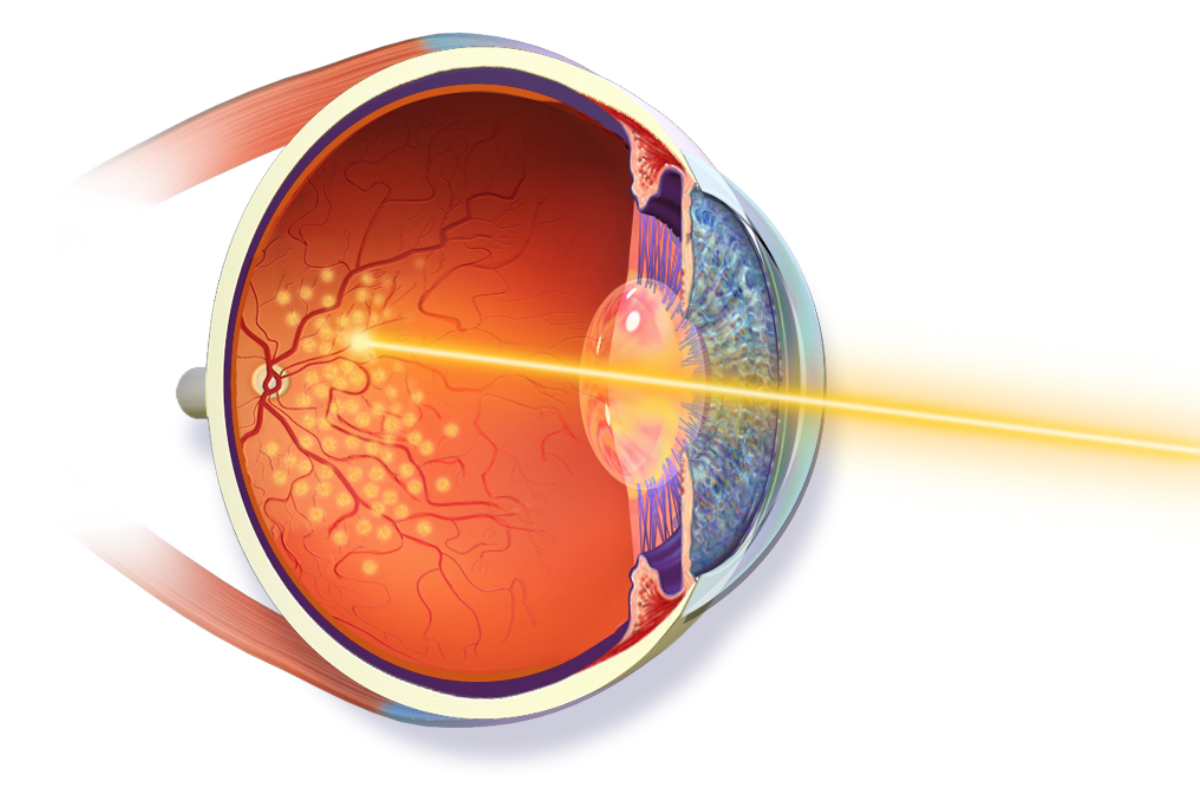

Currently, there is no cure for dry macular degeneration. However, certain steps can help slow down the progression of vision loss. These include:
• Avoiding smoking and exposure to tobacco smoke.
• Maintaining a healthy diet.
• Managing other medical conditions.
• Maintaining a healthy weight and engaging in regular exercise.
• Regular eye exams to monitor the condition.
Laser photocoagulation is a laser surgery technique used to treat late-stage macular degeneration. It helps prevent vision loss by sealing leaky blood vessels.

Services
Our Services For
• Panvel
• New Panvel
• Karanjade
• Kalamboli
• Kamothe
• Kharghar
Contact Us
9022070303
shitutmedicos@gmail.com
KK House, Plot no. 213A, Vishrali Naka, opposite Prashant Lodge, Panvel, Navi Mumbai, Maharashtra 410206
©2023.akshayeyeclinic.com// All Rights Reserved